ZTERM 2000 File Transfer allows files to be sent from the PC to the host system or from the host system to the PC. ZTERM 2000 uses two different approaches for sending files depending on how the connection is made to the host system.
For Network or Dial-Up Networking connections using TCP/IP, ZTERM 2000 uses the standard File Transfer Protocol, commonly referred to as FTP. FTP transfers are very fast, error free and support "wildcard" transfers, allowing the transfer of multiple files.
For Serial and Modem connections between ZTERM 2000 and Alpha Micro AMOS computers, a transfer utility called ZTXFER is provided with ZTERM 2000. This allows high-speed and error free transfers. For Serial and Modem connections to Unix machines, ZTERM supports many standard protocols including X-Modem, Y-Modem and Z-Modem.
See the following topics for information on the two types of file transfer.
When you initiate a file transfer, the following will be displayed:
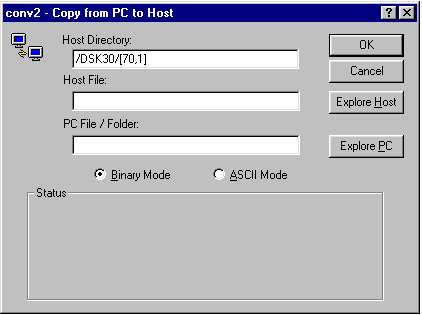
Host Directory: Enter the name of the directory on the host computer you want to transmit to or receive files from. The change to the new directory is made when you move off this field, so if you specify a directory that doesn't exist or you don't have access rights to, an error will be displayed then.
Host File: Enter the name or names of the files on the host to transmit or receive from your PC. Multiple filenames should be separated with a space or you can enter the wildcard characters, * and ?. You can also graphically select files using the Explore Host button next to this text box.
PC File / Folder:
OK: Click this button to start the file transfer once the file names have been entered.
Cancel: Click this button to cancel the transfer or to abort a transfer that's in progress.
Explore Host: Click this button to graphically select remote files to transfer. This option is only available with FTP transfers.
Explore PC: Click this button to graphically select the PC files to transfer.
Binary Mode / ASCII Mode:
Status: This area displays the status of the transfer, including the number of bytes to transfer, bytes remaining and the average transfer rate.